The main results obtained during last years:
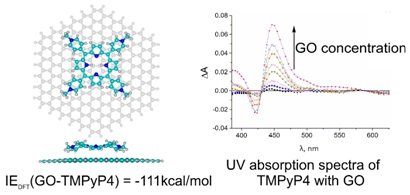 |
The adsorption of cationic porphyrin (TMPyP4) on graphene/graphene oxide was studied using spectroscopy and DFT calculations. The analysis revealed significant structural and spectral transformations of TMPyP4 upon adsorption. The binding of TMPyP4 (–111.0 kcal/mol) is significantly stronger than that of neutral TPP (–22.6 kcal/mol) due to additional cation-π interactions. Adsorption causes a flattening of the porphyrin core and twisting of the side rings, which is accompanied by a red shift of the Soré band. DFT calculations revealed regions of negative potential near the porphyrin adsorption site. J.of Molecular Structure (2021) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.131056 |
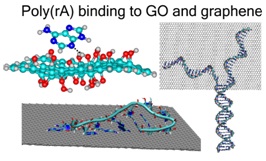 |
The adsorption of poly(rA) onto graphene oxide (GO) was investigated by atomic force microscopy (AFM) and UV absorption spectroscopy. GO was found to induce the self-assembly of single-stranded poly(rA) into a duplex structure (A-motif) at neutral pH, as confirmed by duplex melting observation and AFM imaging. A model for duplex adsorption onto GO was proposed. MD simulations showed how poly(rA) interacts non-covalently with GO. DFT calculations determined the equilibrium structures and interaction energies of the complexes of the nitrogenous base adenine with various oxygen functional groups of GO. J. of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics (2022) DOI: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1814869 |
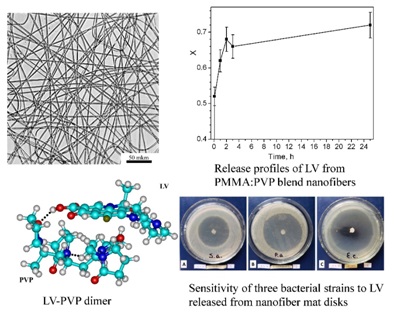 |
Biocompatible nanofibrous mats were fabricated by electrospinning a mixture of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) loaded with levofloxacin (LV). Drug release studies showed that PVP promotes drug incorporation and rapid release, while PMMA provides mechanical stability, ensures insolubility in water, leaving a stable framework suitable for wound dressing. DFT calculation showed the formation of non-covalent complexes between LV and PVP, which affects drug release. The nanofibrous mats demonstrated antibacterial activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, with the release of the LV being more effective against E. coliB than S. aureus and P. aeruginosa, indicating their potential use as antibacterial materials. Mater. Res. Express (2025) https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/adec42 |
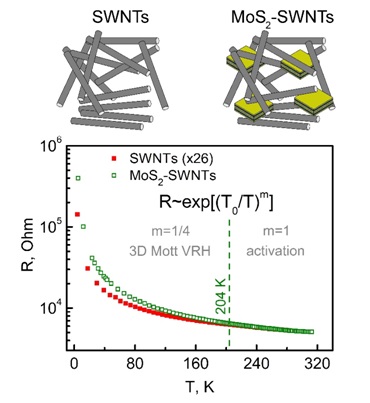 |
It was found that the electrical conductivity of the composite of single-walled carbon nanotubes with molybdenum disulfide nanosheets (SWNTs-MoS2) is primarily due to the nanotubes. The analysis of the temperature dependence of the electrical resistance of the film and comparison with the SWNTs film proves that the same electron transport mechanisms operate in both samples, namely the three-dimensional Mott model at low temperatures (~5-204 K) and the activation model at higher temperatures. Structural changes in the composite compared to the nanotube film, which are associated with the intercalation of MoS2, affect the parameters of electron transport. This effect is more significant at low temperatures. Low Temp. Phys. (2022) https://doi.org/10.1063/10.0009737 |
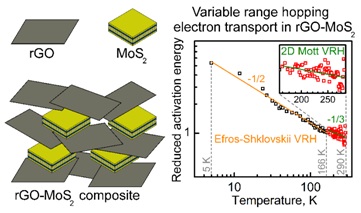 |
The electronic transport in GO–MoS2 composites obtained by vacuum filtration was investigated by analyzing the resistance R(T) in the range of 5–290 K. Two conduction regimes were identified: a variable-range Efros–Shklovsky transition (ES-VRH) at low temperatures and a transition to 2D Mott VRH above 166 K. The approximation of the R(T) data allowed us to determine the localization length, density of states, and Coulomb band gap and compare them with the parameters for the rGO film. The results show that the transport occurs predominantly throughout the rGO nanosheets, while the MoS2 nanosheets modify the ordering of the rGO nanosheets and change their dielectric environment, affecting the transport parameters. Applied Physics A 2025 DOI: 10.1007/s00339-025-08302-7 |
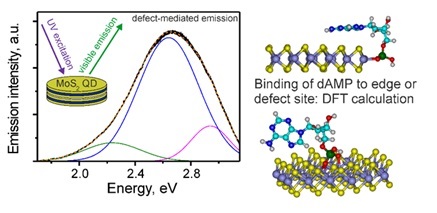 |
Luminescence in the visible range was observed for the first time from MoS2 quantum dots surrounded by nucleotides. It was shown that the dominant contribution to the luminescence is made by defects. DFT calculations showed that dAMP adsorbs mainly at the edges and defects of MoS2 quantum dots, where the coordination bonds with Mo atoms are supplemented by π-π-stacking interactions. Such double binding provides increased stability of the complex and significant interaction energy. This is especially true for quantum dots that have a higher ratio of atoms at the edge of the sheet to atoms on the surface. This observation expands the potential applications of MoS2 quantum dots in the visualization of biological objects and optoelectronics. J. Nanopart. Res. 2024 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-024-06144-7 |
 |
It was shown that the adsorption of single-stranded RNA on the single-walled carbon nanotube (SWNT) and the following hybridization with a complementary strand to form a duplex is not complete because of the strong binding of polymers with the nanotube surface; ChemPhysPhysChem, (2008) 9, 2872, Nanoscale Research Lett. (2014) 9, 157, J. Phys. Chem. C, (2015) 119, 11991 |
 |
It was found that the adsorption of the unordered, flexible polynucleotide onto the carbon nanotube is less effective than the ordered polynucleotides; J. Phys. Chem. B, (2013) 117, 2636 |
 |
First observation of the effect hypochromism of carbon nanotubes (decreasing the intensity of the light absorption in the UV region), which is caused by dipole-dipole interaction in the excited states between the π-π systems of nanotubes and nucleobases of polynucleotides or DNA adsorbed to the nanotube surface; Carbon (2010) 48, 3682 |
 |
A raw of short polynucleotides with decreasing of their energy interaction with carbon nanotube (d(T)25>d(C)25>d(A)25≈d(G)25) is build and showed that the hydroxyl group in the ribose of the polyribonucleotide reduces both its rate of adsorption on the nanotube and the interaction energy between them; J. Phys. Chem. B (2011) 115, 9271 |
 |
The formation of the nanoassembly in aqueous suspension formed by carbon nanotubes with adsorbed anionic polymers (RNA) which is induced by i) cationic porphyrin or ii) the biopolymer hybridization was firstly observed; J. Mat. Chem. (2012) 22 10795, Mol.Cryst. Liq.Cryst. (2008) 497, 339, Fullerenes, Nanotubes, and Carbon Nanostructures, (2010) 18531) |
 |
The possibility of individual SWNTs alignment in polystyrene or in gelatin stretched films was shown; the control of the nanotube alignment was carried out by polarized resonance Raman and absorption spectroscopy. Adv. Funct. Mater. (2012), 22, 2177; Physica E 93 (2017) 92. |
 |
The interaction between polynucleotide (poly(rC)) and graphene oxide (GO) is studied. Spectral shifts of the electronic and vibrational bands of the poly(rC) and changes of their thermostability due to the adsorption on GO are observed. Molecular dynamics simulation of the adsorption process of the r(C)10 and r(C)30 oligomers on graphene demonstrates their disordering due to the π-π stacking of cytosines on graphene. When cytosine is adsorbed to graphene oxide, their complex is additionally stabilized by H-bonding. The obtained information about the adsorption of DNA/RNA strands on GO can be useful for the development of novel genosensors, nanosized scaffolds for drug delivery, and other applications in nanomedicine. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 18221 |
 |
It was shown that the cation-π interaction significantly enhances the binding energy of cationic chromophores, positively charged nucleobases with the carbon nanotube surface and its curvature changes their structures during adsorption; J. Phys. Chem. C (2010), 114, 16215, J. Phys. Chem. C (2012), 116, 20579; J. Mol. Graph. and Modelling (2016) 70, 77 |
 |
Nanostructures formed by linear heterocyclic molecules (such as imidazophenazine and its derivatives) with the nanotubes and/or graphene were studied and the effect of the curvature of the carbon surface and the side groups in the structure of these molecules on the binding energy was revealed, as well as the opportunity to vary the polarizability of graphene and nanotubes by these molecules. ChemPhysChem (2016) 17, 1204; Chem. Phys. (2017) 483-484, 68 |
 |
The influence of the curvature of the carbon nanotube surface on the energy interaction between the Watson-Crick pairs of nucleic acids was studied; Chem.Phys.Lett. (2014) 610-611, 186 |
 |
The structures of hybrids formed by porphin and meso-5,10,15,20-tetraphenyl porphyrin (TPP) with graphene and the corresponding intermolecular interaction energies are studied with the DFT and molecular dynamics calculations. The influence of the peripheral rings arranged around the porphyrin core in the TPP structure on its interaction energy with graphene upon the TPP adsorption is analyzed. Computational and Theoretical Chemistry 1133 (2018) 1–6 |
 |
A significant increase in the intensity of the luminescence from semiconducting SWNTs in aqueous suspensions after doping cysteine was first observed, it was shown that doping with other amino acids has considerably less impact on the nanotube luminescence; Chem. Phys. Lett. (2015) 623, 51, J. Fluoresc. (2016) 26 1951, Materials Chem.Phys. (2017) 186, 131, Nanoscale Research Lett. (2016) 11490 |
 |
It was shown that the variation of the density of the polymer coverage of the surface of semiconducting carbon nanotubes in aqueous suspension allows to increase the sensitivity of the nanotube luminescence to the biomolecule doping; Optics and Spectroscopy (2014) 117, 428, Ukr. Phys. Journ. (2016) 61, 932, Materials Chem.Phys. (2017) 186, 131 |
 |
The exciton energy transfer between the isolated carbon nanotubes in nanoassembly formed by cationic porphyrin was firstly observed and studied. Phys.Chem.Chem.Phys. (2014) 16, 10914 |
 |
It was shown that the redox active molecule (e.g. dithiothreitol) can be used to control the ordered or disordered conformation of biopolymer on the carbon nanotube and serve as a molecular probe to detect the surface defects on the nanotubes exploiting the luminescence from semiconducting nanotubes; Chem.Phys. (2014) 438, 23. |
 |
It was revealed that the nanotube emission is less sensitive to the glutathione (GSH) impact compared to cysteine doping. Experiments with other thiol-containing compounds as DTT and DTE showed a tendency for nanotube to increase the emission larger using a compound with lower redox potential (stronger reducer). A row DTT>DTE>cysteine>GSH was build that shows increasing the emission intensity induced by thiols. Chem.Phys (2019) 516, 218-224 |
 |
The graphene oxide-single walled carbon nanotube (GO-SWNT) hybrids prepared in aqueous suspension and films obtained by vacuum filtration are studied with UV-IR absorption spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and computer simulation. Low temperature measurements of conductivity of these films in the temperature range 5-291 K were also performed. We have found spectroscopic manifestation of the interaction between GO and SWNT in the hybrid, estimated the interaction energy between components, revealed the conductivity in the composite film although in the GO film a noticeable conductivity was not observed. The decrease in the conductivity with lowering of temperature indicates that this dependence is similar with the conductivity observed in disorder semiconducting systems. Low Temperature Physics 2019 |
 |
The composite films of 5-halogen substituted uracils (5-fluorouracil, 5-chlorouracil) with graphene oxide were firstly obtained and it was shown that the modes associated with the vibrations of NH groups are most sensitive to changes in the structure of composite films. Low Temperature Physics 43 (3), 2017, 400; Low Temperature Physics 44 (8), 2018, 847. |
 |
For the first time the populations of main structural isomers of 2’-deoxyadenosine and adenosine were estimated, its characteristic spectral bands were established and it was shown that purine nucleosides have stronger intramolecular H-bonds than the pyrimidine ones. Low Temperature Physics 40 (6), 2014, 565; Low Temperature Physics 41 (11), 2015, 936; |
 |
Formation of stable extended self-assembly of new tricationic meso-porphyrin on inorganic polyphosphate (mixture of J- and H-aggregates, several hundred nanometers in diameter) was revealed. Spectroscopic properties and structural characteristics of the aggregates were determined, their most favorable structures was calculated using DFT method. Biophys. Chem. (2014) 185, 39. |
 |
It was shown that increased anticancer activity of novel zinc metallated porphyrin-imidazophenazine conjugate can be conditioned by the double stabilization of the quadruplex poly(G) by both components of the hybrid. The incorporation of the porphyrin moiety of the conjugate into the poly(G) groove is enhanced by additional intercalation of the phenazine moiety between the guanine bases, that induce inhibition of the telomerase activity and suppress the growth of cancer cells. J. Fluoresc. (2015) 25, 1897. |
 |
Evidences of preservation of the quasi-cyclic or quasi-helical self-organization of the PEG polymer chain around the protonated Cytosine nitrogen base on their noncovalent complex transfer from the liquid to the gas phase are obtained by electrospray mass spectrometry and molecular dynamic simulation. J. Analyt. Chem. (2015) 70, 1533.doi: 10.1134/S1061934815130110s |
 |
Monomer/dimer dependent modulation of reduction activity of the cationic dye methylene blue adsorbed on negatively charged surfactsnt nanolayers is revealed by a novel mass spectrometric approach. Occurrence of reduction for dimers and its absence for monomer agrees with varied biological effects of the dye in photodynamic therapy. RSC Advances (2014) 4, 60260. doi:10.1039/C4RA09592H |
 |
Formation of silver nanoclusters Agn+ in polyether media is revealed by means of mass spectrometry, mechanisms of Agn formation are determined, which include Ag+ wrapping by a polyether chain. Intermediate hydrogen atom-containing nanoclusters AgnH+ (n=2,4,6) are detected for the first time. J. Analyt. Chem. (2017) 72, 1289, doi:10.1134/S1061934817130032; J. Analyt. Chem. (2012) 67, 987. |
 |
In the framework of a problem of combined drugs actions a competition between antimalarial artemisinin-type agents and aspirin for binding with phospholipid membranes was revealed by means of electrospray mass spectrometry and quantum chemical modelling. This means that membranotropic activity of artemisin-type agents and aspirin is modified under their combined usage. Chem. Phys., (2015), 455, 81, doi:10.1016/j.chemphys.2015.04.014 |
 |
Formation of stable noncovalent complexes of cardioprotective medicine flokalin with amino acids Lyz and Thr was revealed by combined mass spectrometric and quantum-mechanical study. Such complexes model biologically significant interactions of the drug with the KATP- membrane channel domains enriched with these two amino acids in biological systems. J. Mol. Struct., (2017), 1146, 441, doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2017.06.007 |